|
|
|
|
|
|
2039
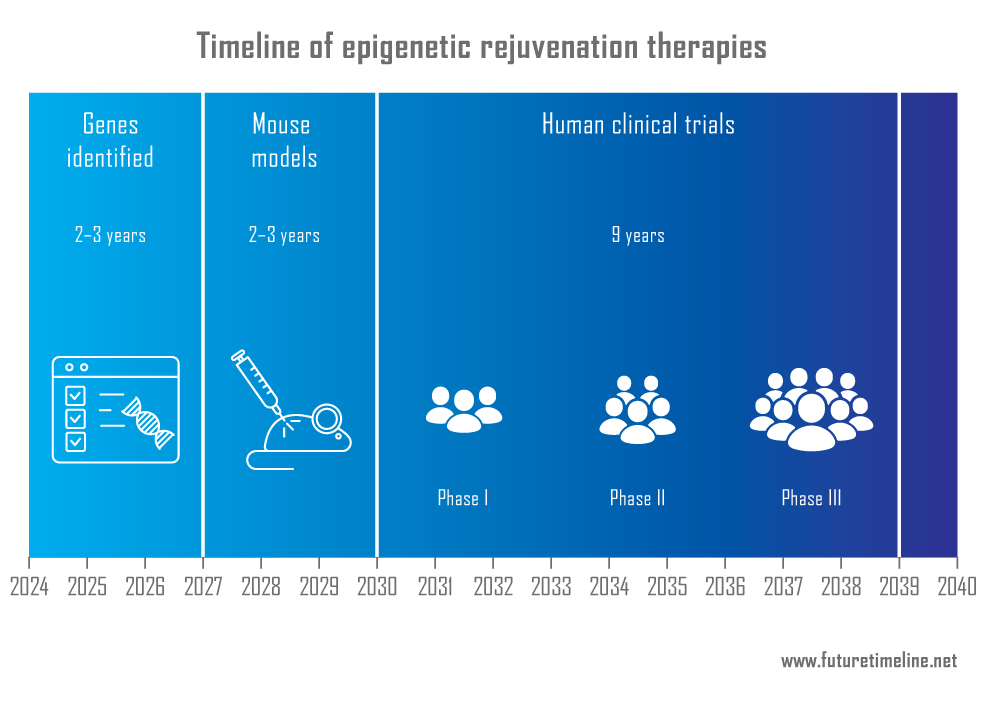
The first generation of epigenetic rejuvenation therapies
During the 2010s and 2020s, researchers began making serious strides towards understanding and treating aspects of the aging process. Some of the areas witnessing progress included telomere extension, senescent cell clearance, mitochondrial repair, and regenerative medicine. Among them, epigenetic rejuvenation emerged as one of the more promising fields.
Epigenetics – a term coined by British scientist Conrad Waddington in 1942 – involves the study of how our genes are turned on and off, without altering the DNA sequence itself, via mechanisms such as DNA methylation and histone modification. These processes have increasingly damaging consequences as a person ages.
In 2013, scientists discovered the epigenetic clock, a way of measuring biological age by tracking DNA methylation levels. This provided a more accurate measure of an organism's age than merely chronological age. Researchers began attempting to "reset" this clock by using transcription factors – a set of proteins able to turn specific genes "on" or "off" by binding to nearby DNA – capable of reprogramming adult cells back to a youthful, pluripotent state.
Early experiments with transcription factors, particularly the Yamanaka factors, showed immense promise in rejuvenating cells.* However, safety concerns arose due to the risk of cancer. The process of reprogramming cells involved significant changes in gene expression, potentially triggering uncontrolled cell growth and tumour formation unless precisely regulated. To address these risks, researchers began working to refine the combinations of factors used, aiming to achieve the rejuvenating effects while minimising the danger of cancer and other adverse effects.
The identification of suitable transcription factors received a major boost in 2023 when scientists began using transformer models and graph neural networks to understand the relationships between genes in real cells in the wet lab. This allowed researchers to create virtual versions of these interactions and see how well they correlated with real-world cells. The discovery process, now made 300 times faster, generated many millions of results within just a few years. This led to mouse model experiments, followed by the start of human clinical trials.
By 2039, the first successful trial data has been published, confirming the safety and efficacy of epigenetic rejuvenation in humans.* These results demonstrate significant improvements in biological age markers and a reduction in age-related diseases. While not a perfect cure, this represents a major leap forward in extending healthy lifespans.
During the 2040s, epigenetic rejuvenation will become more widely available to the public, offering a partial reversal for certain aspects of aging – such as improved skin elasticity, better mobility and joint function, and resilience against cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. As ongoing research continues to build on and refine these treatments, the potential for even more comprehensive anti-aging solutions draws closer. Whole-body rejuvenation moves from science fiction to science fact during the second half of the century, heralding a world in which age-related decline is a thing of the past.
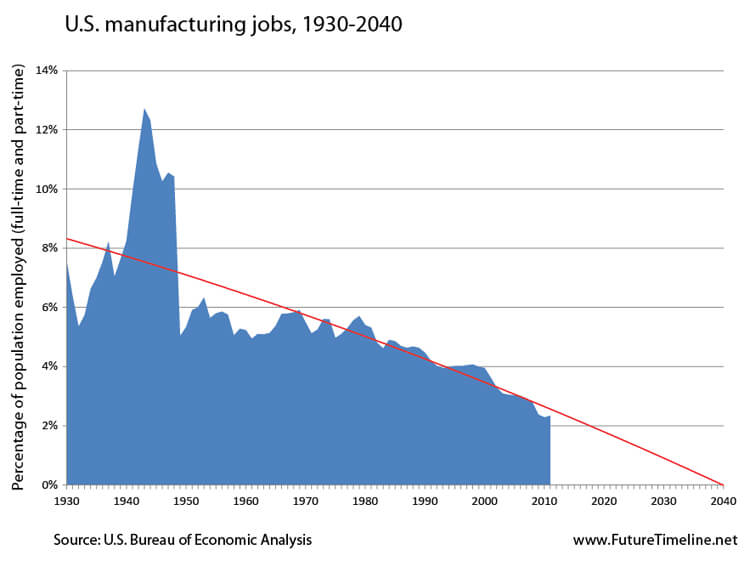
Manufacturing jobs have largely disappeared in the West
In the United States and most other developed nations, manufacturing has gone the same way as agriculture – vitally important, yet employing very few people. Robots, automation and 3D printing, now sufficiently perfected after decades of development, have taken over a wide range of roles once performed by humans.*** As China and other emerging nations make the transition to service-based economies, they too will experience this trend in the not-too-distant future.
Australia's national symbol, the koala, faces extinction
By this date, the koala population in Australia has dwindled to almost nothing, due to the combined impacts of drought, disease, climate change and and loss of natural habitat.* Only those in captivity now remain.

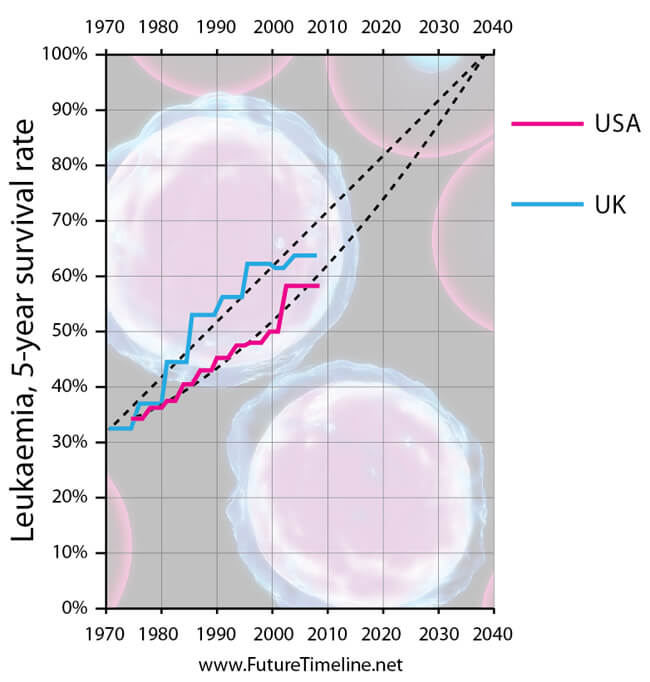
Five-year survival rates for leukaemia are approaching 100%
Leukaemia is a cancer of the blood or bone marrow, characterised by an abnormal increase in the number of immature white blood cells, called "blasts". In 2008, there were 350,000 new cases worldwide, and 257,000 deaths from the disease, placing it within the top 10 most common type of cancer deaths.
However, treatments improved greatly over the decades, with survival rates showing a consistent upward trend. Gene therapy was among the most successful new approaches. One such method turned a patient's own T-cells into cancer-targeting attackers. In one study, conducted between 2010 and 2011, two of three patients remained cancer-free after a year.* By 2039, five-year survival rates in many countries are reaching 100%.**
Extreme heatwaves are commonplace in the U.S.
The previous five decades were all the hottest on record – each surpassing the last. Extreme heatwaves are now having a serious impact on agricultural yields and human health. This is a particular problem in the American West. From 2030 to 2039, most areas of Utah, Colorado, Arizona and New Mexico have at least seven summers equal to the hottest season ever recorded between 1951 and 1999. The hottest daily temperatures of the year from 1980 to 1999 have become twice as frequent. There are persistent, drier conditions around the country, with substantial reductions in soil moisture and an accompanying rise in forest fires.*

Credit: dl91m
« 2038 |
⇡ Back to top ⇡ |
2040 » |
If you enjoy our content, please consider sharing it:
References
1 Age of skin cells reversed by 30 years, Future Timeline Blog:
https://futuretimeline.net/blog/2022/04/8-age-of-skin-cells-reversed-by-30-years.htm
Accessed 27th July 2024.
2 First generation of anti-aging treatments may arrive before 2040, Future Timeline Blog:
https://www.futuretimeline.net/videos/98-reverse-aging-2040.htm
Accessed 27th July 2024.
3 Table 6.4A-D. Full-Time and Part-Time Employees by Industry (A), National Income and Product Accounts Tables, US Bureau of Economic Analysis:
https://apps.bea.gov/iTable/?reqid=19&step=2&isuri=1&categories=survey
Accessed 27th December 2023.
4 Rethink Robotics aims to revolutionise manufacturing with humanoid robot, Future Timeline Blog:
https://www.futuretimeline.net/blog/2012/09/18.htm
Accessed 13th June 2013.
5 How Technology Is Destroying Jobs, MIT Technology Review:
https://www.technologyreview.com/2013/06/12/178008/how-technology-is-destroying-jobs/
Accessed 11th June 2020.
6 Koalas 'extinct within 30 years' after chlamydia outbreak, The
Telegraph:
http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/australiaandthepacific/australia/6537179/Koalas-extinct-within-30-years-after-chlamydia-outbreak.html
Accessed 12th November 2009.
7 New leukemia therapy destroys cancer by turning blood cells into "assassins", CBS:
http://www.cbsnews.com/8301-504763_162-20091135-10391704.html
Accessed 7th October 2012.
8 Browse the SEER Cancer Statistics Review 1975-2009 (Vintage 2009 Populations), National Cancer Institute:
http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2009_pops09/browse_csr.php
Accessed 7th October 2012.
9 Leukaemia survival statistics, Cancer Research UK:
http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/cancer-info/cancerstats/types/leukaemia/survival/
Accessed 7th October 2012.
10 Heat waves and extremely high temperatures could be commonplace in
the U.S. by 2039, Stanford study finds, Stanford News Service:
http://news.stanford.edu/pr/2010/pr-extreme-heat-study-070810.html
Accessed 19th August 2010.
![[+]](https://www.futuretimeline.net/images/buttons/expand-symbol.gif)